Are you experiencing dryness in your mouth? Do you find yourself constantly reaching for water or struggling to speak without feeling parched? If so, you are not alone. Mouth dryness is a common problem that affects people of all ages. But what are the causes of mouth dryness? This article explores the causes of mouth dryness and provides some remedies to alleviate the symptoms.
What is Mouth Dryness ?
Before delving into the causes of mouth dryness, it’s important to understand about mouth dryness.
Mouth dryness, also known as xerostomia, can be a frustrating and uncomfortable condition. It is a condition where the salivary glands in the mouth do not produce enough saliva, causing discomfort and difficulty in speaking, swallowing, and eating (1).
Mouth dryness can lead to oral health issues such as bad breath, tooth decay, and gum disease. Treatment options typically involve addressing the underlying cause, increasing saliva production, and managing symptoms to alleviate discomfort. In some cases, dry mouth can even lead to infections and other serious health problems (2).
Symptoms of Dry Mouth
Dry mouth, also known as xerostomia, can cause a variety of symptoms, including (1, 2)
- A sticky or dry feeling in the mouth,
- Difficulty speaking or swallowing,
- Sore throat or hoarseness,
- Burning or tingling sensation in the mouth,
- Cracked lips or corners of the mouth,
- Bad breath,
- Difficulty chewing or tasting food,
- Increased thirst,
- Mouth sores or infections,
- Dental problems such as tooth decay or gum disease.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult a dentist or healthcare professional to diagnose and treat the underlying cause of dry mouth.
So, what causes dry mouth? Let’s explore some of the most common factors.
The Top 10 Surprising Causes of Mouth Dryness (Oral Dryness)

Oral dryness can be caused by various factors such as medication use, dehydration, nerve damage, autoimmune disorders, cancer treatments (radiotherapy), and aging. Here are the top 10 causes of dry mouth-
Dehydration
Dehydration is a common cause of mouth dryness, especially during hot weather or intense physical activities. When your body doesn’t have enough water, it can’t produce enough saliva, which can leave your mouth feeling dry and uncomfortable (3).
If you are experiencing dry mouth due to dehydration, the best thing you can do is to drink plenty of fluids, especially water.
Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water a day, and more if you are sweating or exercising. You can also try drinking sports drinks or coconut water to help replenish electrolytes lost through sweating.
In addition to drinking fluids, you can also try sucking on ice chips or sugar-free hard candies to help stimulate saliva production.
Chewing sugar-free gum can also help, as the act of chewing can help stimulate the production of saliva.
If you are experiencing severe dehydration or are unable to drink fluids due to nausea or vomiting, seek medical attention immediately. Dehydration can be a serious condition that requires prompt treatment to prevent complications.
Medications
Dry mouth or oral dryness is a common side effect of many medications (1). This can be particularly problematic for those who rely on regular medication to manage chronic health conditions.
Dry mouth can lead to a number of issues, including difficulty speaking and swallowing, oral infections, and tooth decay.
There are a number of medications that can cause dry mouth, including antihistamines, antidepressants, and medications used to treat high blood pressure, among others.
If you are experiencing dry mouth as a side effect of a medication, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider, as they may be able to adjust your medication or provide additional treatments to help manage your symptoms.
Medical Conditions
Oral dryness can be a symptom of a number of medical conditions. Some of the most common conditions that can cause dry mouth include (4, 5)
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves that control the salivary glands, leading to decreased saliva production and dry mouth.
- Sjogren’s syndrome: This is an autoimmune disorder that attacks the glands that produce saliva and tears, resulting in dry mouth and dry eyes.
- Parkinson’s disease: This neurological disorder can cause problems with swallowing and decreased saliva production, leading to dry mouth.
- HIV/AIDS: The virus that causes HIV can damage the salivary glands, leading to dry mouth and an increased risk of oral infections.
- Alzheimer’s disease: This progressive neurological disorder can affect the nerves that control the salivary glands, leading to dry mouth and difficulty swallowing.
- Cystic fibrosis: It is a genetic disorder that harms the respiratory and digestive systems. It can also impact the function of salivary glands, leading to dry mouth. The medications used to treat cystic fibrosis can also worsen dry mouth.
If you are experiencing dry mouth as a symptom of a medical condition, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider.
Learn more: Discover Quick and Easy Home Remedies for Tonsillitis Pain Relief
Aging
Dry mouth is a common problem in older adults. As we age, our bodies produce less saliva, which can lead to dry mouth and a range of associated symptoms (6).
There are a number of factors that can contribute to dry mouth in older adults, including medications, chronic medical conditions, and changes in diet and lifestyle.
In addition to these factors, older adults may also experience changes in their diet or lifestyle that can lead to dry mouth. For example, older adults may drink less water or eat fewer fruits and vegetables, which can reduce saliva production.
They may also be more likely to drink alcohol or smoke, both of which can exacerbate dry mouth.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy for head and neck cancer can damage the salivary glands, leading to a condition known as radiation-induced xerostomia, or dry mouth.
This can be a significant problem for cancer survivors, as dry mouth can lead to difficulty speaking and swallowing, dental decay, and an increased risk of oral infections (7).
If you are undergoing radiation therapy for head and neck cancer, your healthcare team will likely take steps to help reduce the risk of dry mouth.
This may include prescribing medications to stimulate saliva production, such as pilocarpine or cevimeline. Your healthcare team may also recommend drinking
Smoking and Tobacco Use
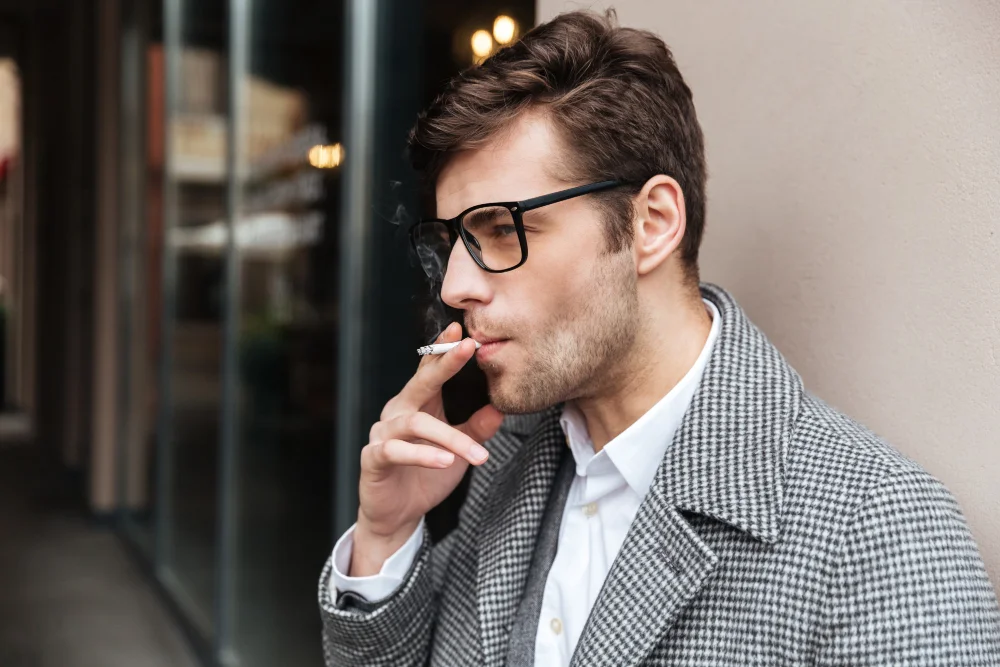

Smoking and tobacco use are known to cause several negative effects on the human body, including dry mouth (8).
Tobacco smoke contains thousands of harmful chemicals, including nicotine, which is a stimulant that can decrease saliva production. When a person smokes or uses tobacco, their mouth becomes dry, and this dryness can persist even after they stop smoking.
Dry mouth can also lead to bad breath, difficulty chewing and swallowing, and an increased risk of developing oral infections.
Quitting smoking and tobacco use can help improve overall oral health and reduce the risk of dry mouth and related complications. Additionally, drinking plenty of water and using sugar-free gum or lozenges can help stimulate saliva production and alleviate dry mouth symptoms.
Nerve Damage
Nerve damage can be a potential cause of dry mouth. The nerves that control the salivary glands may be damaged due to various reasons such as radiation therapy, chemotherapy, diabetes, or autoimmune diseases (9).
When these nerves are damaged, the salivary glands may not receive the proper signals to produce enough saliva, leading to dry mouth.
If you suspect that your dry mouth is caused by nerve damage, it is important to discuss with your healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Autoimmune Disorders
In autoimmune disorders, the immune system may attack the salivary glands, causing inflammation and damage. This can lead to a decrease in saliva production and dry mouth (10).
Some autoimmune disorders that are commonly associated with dry mouth include Sjögren’s syndrome, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and scleroderma.
Mouth Breathing
Mouth breathing can also cause dry mouth, as it reduces the amount of saliva production in the mouth. When we breathe through our nose, the air is warmed, moistened, and filtered before it enters the lungs.
On the other hand, when we breathe through our mouth, the air bypasses the nasal passages and enters the mouth and throat directly, which can cause the tissues to dry out.
Chronic mouth breathing can cause the salivary glands to become dehydrated and reduce the amount of saliva in the mouth. This can lead to dry mouth, which can cause discomfort and increase the risk of dental problems.
In addition to dry mouth, mouth breathing can also cause other health problems, such as snoring, sleep apnea, and bad breath. It can also cause the muscles in the face to become weaker, which can affect facial development in children.
Snoring and Sleep Apnea
Snoring and sleep apnea can cause dry mouth because they disrupt normal breathing during sleep. When a person snores or has sleep apnea, their airway becomes partially or completely blocked, leading to a decrease in airflow and oxygen intake (11).
This can cause the mouth and throat to become dry because the normal production of saliva is reduced.
Additionally, people with sleep apnea may breathe through their mouth more frequently, which can further contribute to dry mouth.
Home remedies for Dry Mouth

Dry mouth is a common condition that can be caused by a variety of factors. Fortunately, there are some home remedies to prevent and alleviate symptoms of dry mouth. Here are some of these (12):
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water and other fluids can help keep your mouth moist and reduce the discomfort of dry mouth. Avoid caffeine and alcohol, which can dehydrate you and worsen dry mouth.
- Chew Gum or Suck on Candy: Chewing sugar-free gum or sucking on sugar-free candy can stimulate saliva production, which can help keep your mouth moist. Be sure to choose sugar-free products to avoid exacerbating dental issues.
- Use a Humidifier: Running a humidifier in your home can help add moisture to the air, which can reduce dry mouth symptoms.
- Practice Good Oral Hygiene: Brushing and flossing regularly can help remove bacteria and food particles that can contribute to dry mouth and dental problems.
- Try Saliva Substitutes: Over-the-counter saliva substitutes can help provide temporary relief of dry mouth symptoms. These products are designed to mimic the properties of saliva and can help keep your mouth moist.
- Adjust Your Diet: Eating foods that are high in water content, such as fruits and vegetables, can help keep your mouth moist. Avoid foods that are spicy, acidic, or high in sugar, which can irritate your mouth and exacerbate dry mouth symptoms.
It’s also important to brush and floss your teeth daily and to get a dental checkup twice per year. Good oral care can help prevent tooth decay and gum disease, which can result from dry mouth.
Learn more- 10 Natural Ways to Get Rid of Red Eyes Without Eye Drops
Learn more- Quick and Easy Ways to Eliminate Bitter Taste in Your Mouth
Dry mouth and tooth decay

Saliva plays an important role in maintaining oral health by washing away food particles, neutralizing acids produced by bacteria, and helping to remineralize tooth enamel.
When there is a lack of saliva, these processes are disrupted, and harmful bacteria can accumulate on the teeth, leading to cavities and other dental problems. Therefore, it is important to address the underlying causes of dry mouth, such as certain medications, medical conditions, or lifestyle factors, and take steps to promote saliva production, such as drinking water, chewing sugar-free gum, and using saliva substitutes or prescription medications.
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are also important for preventing and treating tooth decay in people with dry mouth.
How to Treat Dry Mouth?
Here are some treatment options for dry mouth:
- Use over-the-counter products: There are various over-the-counter products available that can help with dry mouth, including mouthwashes, lozenges, and gels. These products can help lubricate the mouth and stimulate saliva production.
- Manage underlying conditions: In some cases, dry mouth may be a side effect of certain medications or an underlying medical condition. Treating these conditions can help alleviate dry mouth symptoms.
- Prescription medications: If over-the-counter products are not effective, prescription medications may be prescribed by a healthcare provider to help stimulate saliva production.
- Surgical Procedures: If dry mouth is caused by an obstruction, such as a tumor, surgical removal of the obstruction may be necessary to relieve symptoms.
- Visit your dentist regularly: Regular dental checkups can help identify and treat dental problems that can cause dry mouth.
Diagnosis of Mouth Dryness
Here are some ways to diagnose mouth dryness:
- Medical history: Your doctor may ask about your medical history, including any medications you are taking, and whether you have had any recent illnesses or surgeries.
- Physical exam: A physical examination of your mouth, including your teeth, gums, and tongue, can help identify any signs of dryness or inflammation.
- Saliva tests: A saliva test may be done to measure the amount of saliva produced in your mouth. This can help determine if your mouth is producing enough saliva or if you have a salivary gland problem.
-
Blood tests: Blood tests may be ordered to check for underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes or Sjogren’s syndrome, that can cause dry mouth.
When to See a Doctor
Here are some signs and symptoms that may indicate that you need to see a doctor:
- Persistent dry mouth: If your mouth continues to feel dry despite your efforts to hydrate and practice good oral hygiene, it may be a sign of an underlying medical condition.
- Difficulty eating or swallowing: Dry mouth can make it difficult to chew, swallow, and speak, which can lead to nutritional deficiencies and social isolation.
- Sore throat or hoarseness: Chronic dry mouth can cause irritation and inflammation of the throat, which can lead to a sore throat or hoarseness.
- Bad breath: A dry mouth can contribute to bad breath, which can be a sign of underlying dental or medical problems.
- Tooth decay or gum disease: Dry mouth can increase your risk for dental problems such as tooth decay and gum disease, which can lead to tooth loss and other complications.
Read more: 10 Natural Ways to Get Rid of Red Eyes Without Eye Drops
Read more- How to Stop Cough at Night: 12 Best Home Remedies
Conclusion
Dry mouth can be caused by various factors such as medication, dehydration, and medical conditions. It can lead to discomfort, difficulty speaking or swallowing, and dental problems.
Managing dry mouth involves staying hydrated, avoiding certain medications, using saliva substitutes, and practicing good oral hygiene. It’s important to speak with a healthcare professional if you experience persistent dry mouth or if it significantly impacts your daily life.

